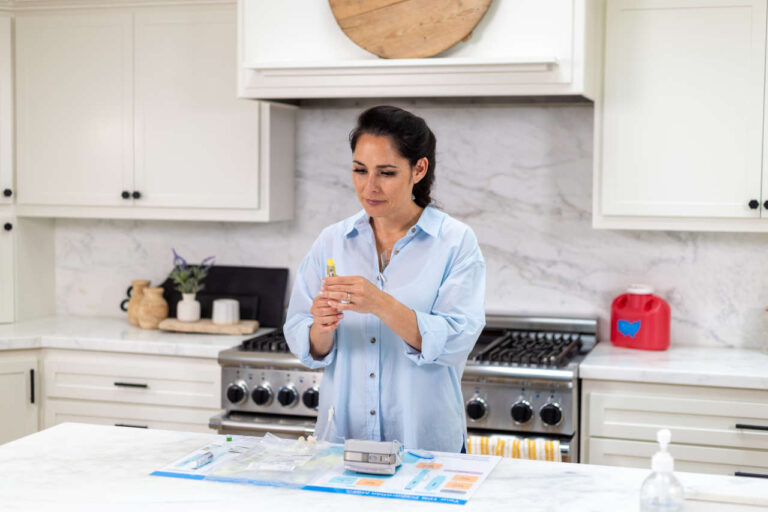
People suffering from long-term illnesses that affect their digestive systems (causing them not to function properly) may require ongoing nutrition support through a route other than the oral one. When all the nutrients that a person needs is delivered intravenously (through the person’s veins), this is referred to as total parenteral nutrition or TPN. TPN therapy can be administered either at the hospital or at the patient’s home. However, receiving TPN at home is usually considered the most convenient way, especially for patients requiring continuous/long-term nutritional care.
Speak to a Specialist About Copay Assistance
What Is TPN Therapy, and Who Needs It?
TPN, also known as total parenteral nutrition, is the intravenous feeding of nutrition to patients who have a compromised digestive system. It is also given to individuals who cannot swallow food, absorb nutrients from meals, or pass the food through their digestive system due to a disorder.
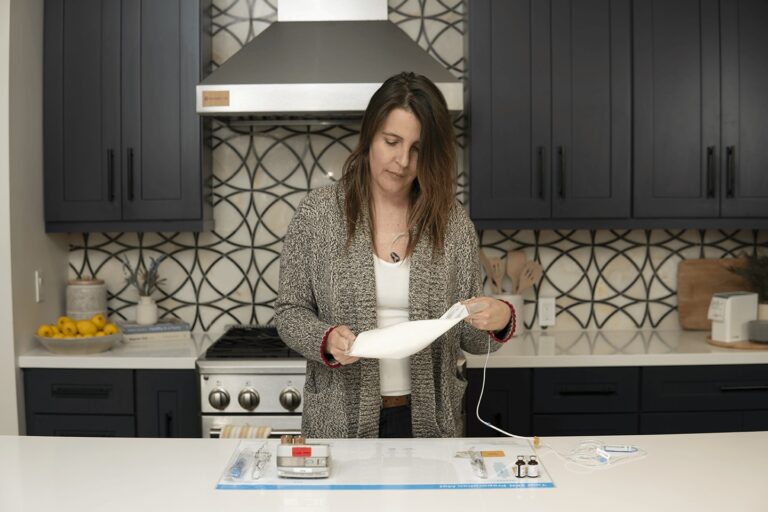
Storage and Handling of TPN Bags
Here are some crucial points that you should consider while storing and handling your TPN bags:
- Store all the TPN bags in the refrigerator. The refrigerator’s temperature should be between 36°F to 46°F. The only exception would be the premixed TPN bags intended for emergency use (usually called Clinimix or Kabiven) which should be stored at room temperature (68°F to 77°F) prior to opening.
- Make sure there is enough space in your refrigerator for storing the TPN bags.
- Store the TPN solution bag on the top shelves of your refrigerator to avoid the spilling of food items onto them.
- Only store TPN bags on clean refrigerator shelves.
- Do NOT store TPN bags in refrigerator doors to avoid subjecting them to temperature variations when the refrigerator door is opened during the day.
How To Warm the TPN Solution Safely
To reduce the chances of experiencing chills, headaches, and discomfort during the infusion, it’s recommended NOT to infuse TPN bags straight after getting them out of the fridge, when the solution is very cold. Follow these simple guidelines to warm the TPN solution before use:
- Take the solution out of the refrigerator and let it get warm on a clean countertop for 2 to 3 hours at room temperature.
- Do not warm the TPN solution using artificial methods like the stove, microwave, oven, direct sunlight, or any other method.
- If you must, you can infuse the TPN bags at cold temperatures, but it may cause discomfort, headaches, and chills.
- You may leave the TPN solution at room temperature for up to 30 hours in total (including the time of infusion).
How To Draw Medications From a Vial or Ampule
In some cases, you might have to add some medications/additives to your TPN bags (e.g., multivitamin supplements) right before you start the infusion. This is usually done to prolong the shelf-life of the TPN bags once they’ve been compounded. There are five simple steps to draw medications or other additives from a vial or ampule and inject them into your TPN bag.
1. Preparation
First, carefully read your medication label and thoroughly review any literature you received with it. By doing this, you will familiarize yourself with all the correct details of handling, storing, and taking the medication you have been prescribed.
Next, clean your work area (the area you will designate to prepare your medication before taking it) and wash your hands with soap and water. Dry your hands with a clean and unused hand towel. Make sure your nails are clean and kept well-trimmed. You can also use an alcohol-based sanitizer if you don’t have access to soap and water, although it is preferable that you wash your hands with soap and water.
AmeriPharma™ Specialty Care
Total Parenteral Nutrition | Leader In TPN Assistance2. Gathering Necessary Supplies
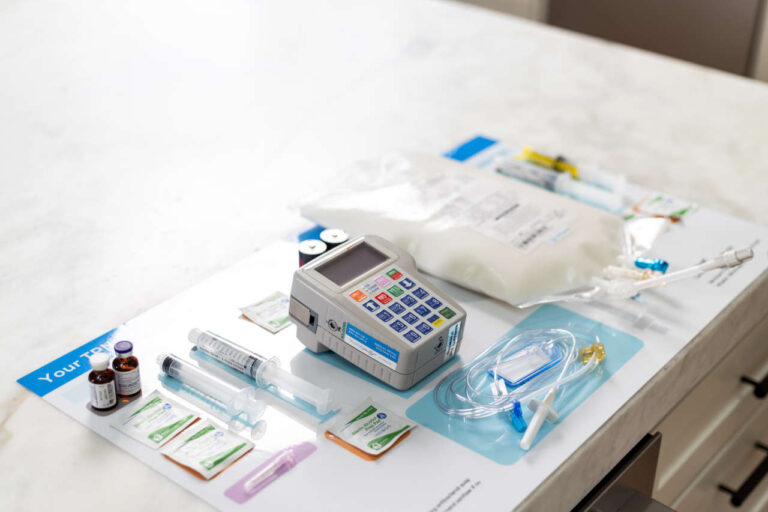
Before drawing and administering the medication, it is essential to gather all necessary supplies. The supplies you will need include:
- Alcohol prep pads
- Medication vials or ampules
- Syringe with needle
- Filter needle and an extra needle (for use with ampules)
- Sharps container
3. Inspecting the Vial/Ampule and Medication Label Before Drawing and Administering the Medicine
Don’t forget to double-check the following for each vial or ampule:
- Expiration date
- Correct dose
- Correct name
- Absence of particles in the solution
4. Drawing Medication
A) For Vials:
- Take off the cap from the vial.
- Using an alcohol pad, wipe the top of the vial, including the rubber stopper, for 15 seconds, and then allow the alcohol to dry to kill any germs, fungus, or bacteria.
- Take the syringe out of its cover. The top part of the syringe should remain sterile, so do not touch it with your hand or allow it to touch any surface. Hold/handle the syringe only from the barrel where the volume gradations are printed.
- Take the needle out of its package, being careful not to touch the needle or the plastic hub right below the needle with your fingers, as these areas should remain sterile.
- Hold the syringe and twist the needle clockwise until the syringe is secured with the needle. Then take the cover off of the needle.
- Before drawing medication into the syringe, first, draw air into the syringe that is equal to the volume of the medicine you will be withdrawing out from the vial. For example, if you have to draw 5 ml of medicine into the vial, first pull the syringe plunger and draw 5 ml of air.
- Insert the syringe needle into the center of the vial’s rubber stopper and push the plunger to dispense the air into the vial.
- With the needle still in the vial, turn the vial upside down and draw the required amount of medicine into the syringe.
- Pull the syringe out of the vial and remove air bubbles from the syringe by holding the syringe straight up. Gently tap on the syringe barrel and push the plunger until all the air bubbles are removed.
- If you are required to add multivitamins to the TPN bag, you will be sent two vials per dose. You can use a single syringe for drawing medication from both vials. There are two ways this can be accomplished:
- Withdraw an amount of air equal to the total amount of medicine to be withdrawn for both vials. Push half the TOTAL amount of air into the first vial, then turn the vial upside down and withdraw the appropriate amount of solution. Then, inject the remaining air into the second vial, turn the vial upside down, and withdraw the required amount of solution from the second vial. After doing this, inject all the contents in the syringe into the TPN bag (see step 5 below).
- Withdraw an amount of air equal to the amount of medicine to be withdrawn from a single vial. Push the air into the vial, then turn the vial upside down and withdraw the solution. Inject the solution into the TPN bag (see step 5 below), and repeat the steps for the second vial.
Ask About TPN Home Infusion
B) For Ampules:
- Tap the top part of the ampule two to three times with your fingers so that the entire liquid settles at the bottom of the ampule.
- Use an alcohol pad to clean the top part of the ampule. Then use a new alcohol pad and wrap it around the top of the ampule.
- With your finger and thumb, break off the top part of the ampule. Make sure to snap it off away from yourself and be careful not to waste any medication. Discard the top part in a sharps container.
- Place the ampule containing the medication straight on a flat surface.
- As described above (in the section for vials), always remove the syringe and needles from their packages while maintaining the sterility of the parts.
- By twisting clockwise, attach the filter needle to the syringe and take off the needle’s plastic cover.
- Insert the filter needle into the ampule.
- Pull the syringe plunger and draw the required amount of medication from the ampule into the syringe (When drawing medication from an ampule, there is no need to withdraw and dispense an equal amount of air as with vials.)
- Remove the syringe from the ampule.
- Carefully place the cover of the needle back on and remove the filter needle from the syringe by turning it counterclockwise.
- Now place a non-filter needle on the syringe.
- To make sure there are no air bubbles in the ampule, hold the syringe and its needle pointing upward. Gently tap on the syringe with your fingers.
- Push the plunger until all air bubbles are removed.
- Proceed to add the medication to the TPN bag.
5. Adding Additives Into the Medication Bag (If Necessary)
If you are required to add additives into the TPN bag (as discussed above), follow these steps:
- Before injecting the additive into the TPN bag, clean the injection port with an alcohol pad for 15 seconds, then allow the alcohol to dry for a few seconds.
- Slowly insert the syringe needle into the rubber end of the injection port, being careful to avoid puncturing the bag (If you puncture a TPN bag by mistake, do not use that bag.)
- Push the syringe plunger and inject the medication into the TPN bag.
- Carefully remove the syringe from the bag and discard it in the sharps container.
- Gently massage and invert the TPN bag to mix the medication with the additives.
Monitoring Yourself
It is important to keep track of your health while you are on TPN therapy. You should always monitor yourself at home and contact your healthcare provider in case of any irregularities.
Here are the vitals you need to record:
- Weight
- Temperature
- Blood sugar level
- Intake
- Output
Speak to a Specialist About Copay Assistance
1. Weight

Check your weight at the same time every day wearing similar articles of clothing and write it down. If you notice any unusual increase or drop in your weight, inform your doctor.
2. Temperature
Check your temperature at the same time every day and write it down. To avoid any false readings, wait for 15 minutes after you eat, drink, or smoke, then measure your temperature. If, on any day, your temperature is above 100.4°F, contact your doctor.
3. Blood Sugar Level (If You Are Diabetic)
Use glucose monitoring equipment like a glucometer to check your blood sugar levels. Both low and high blood sugar levels can be harmful. If you don’t know how to use the equipment, you should learn and perform it in the presence of your doctor a few times before doing it on your own.
- Your healthcare provider will set goals for your blood sugar levels. Make sure that you are always meeting these goals. If your levels get higher or lower than the set goal target, you must notify your doctor right away.
- If you have diabetes, your doctor may instruct you on using insulin depending on your blood sugar levels.
- Make sure your blood sugar levels are not below 70 mg/dl.
Contact your doctor if your blood sugar levels are too high or too low.
4. Intake
Keep track of how much liquid is getting into your body:
- Oral Fluid Intake: This includes beverages such as coffee, tea, water, carbonated beverages, fruit juices or drinks, and cream. Soup, Jell-O, popsicles, and ice chips/cubes are also considered fluids.
- Intravenous (IV) Intake: This includes the total amount of TPN solution infused as well as any other IV fluids infused, such as medications (e.g., IV antibiotics) and lipids.
- Total Intake: This is calculated by adding all ORAL fluids and IV fluids consumed or infused for the 24-hour period. Ideally, your total intake (both IV and oral) should be 500 ml GREATER than your total output each day (Your doctor may have a different goal set for your fluid intake minus output value.)
5. Output
Keep track of how much liquid, including urine, stool, vomit, and fistula drainage you excrete. If the amount is unusual, contact your healthcare provider.
AmeriPharma™ Specialty Care
Total Parenteral Nutrition | Leader In TPN AssistanceHow To Take Care Of Your Catheter And Keep It Safe
Safe handling of infusion is of utmost importance, as negligence can cause infections and other complications.
Here are some tips on how to handle your catheter and infusion:
- Clean your work area and make sure you have enough space before setting up the TPN medication and infusion supplies.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds before touching the catheter, supplies, or medication.
- Before connecting any medication supplies, use an alcohol pad to rub the catheter injection cap for 15 seconds.
- Do not touch the sterile syringe needle or the end of the tubing. If you touch a syringe needle by accident, throw it away in the sharps container and use a new, sterile syringe.
- Do not use any sharp objects like scissors, knives, or pins near the TPN bags, tubings, or the catheter.
- Keep the area around your catheter dry, and cover it up when you bathe or shower.
- Before and after infusing your medication, flush your catheter with the recommended amount of normal saline.
- If directed, flush your catheter with heparin after the saline flush as per the SASH protocol.
Conclusion
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) is administered to patients suffering from gastrointestinal compromises or who cannot take food by oral administration. Many patients who are on TPN therapy for the long term prefer getting their infusions at home.
You can easily administer TPN at home without needing to visit the hospital every day. However, it is important to ensure the safe handling of catheters, supplies, and medication to avoid infections and other complications. Make sure you learn and familiarize yourself well with the steps of safe and effective TPN handling and administration before opting for home therapy.