Your body needs a certain balance of nutrients and fluids to function properly. Inadequate nutrition can impair your health, causing hormonal imbalances and a compromised immune system, among many other disorders. Not everyone is able to obtain essential nutrients through food. This is when TPN therapy can be considered.
Those unable to eat or digest food will need TPN treatments to meet their daily nutritional requirements. This dependency on regular infusions can be challenging. However, learning more about it can make the process easier. Below is a complete review guide to TPN infusions for those who are new to this therapy.
What is TPN?
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) involves delivering vital nutrients straight to the bloodstream through an IV drip. It’s also known as intravenous feeding or IV nutrition feeding.
TPN therapy allows patients without a functioning gastrointestinal (GI) tract to receive the necessary nourishment to survive. It provides all the nutrients that your body is unable to absorb through a regular diet and helps prevent malnutrition.
What Are the Ingredients in a TPN Bag?
A TPN bag consists of the macronutrients and micronutrients your body needs to function. The exact amount of each nutrient will differ for each person. Your doctor and pharmacist can determine this amount and adjust the formula based on your health condition and individual needs.
TPN therapy usually contains a combination of the following nutrients:
- Fats
- Water
- Proteins
- Minerals
- Vitamins
- Electrolytes
- Carbohydrates
Each of these ingredients plays a vital role in maintaining your health. For instance, electrolytes help your metabolic processes, while proteins feed your muscles. Collectively, they give you the energy you need to survive and stay healthy.
Who Needs to Receive TPN Treatment?
TPN infusions can supplement tube feedings or be an alternative nutrition source for those who can’t eat or absorb food. Many undernourished patients in long-term rehab and healthcare facilities can benefit from this form of therapy as they recover.
Others may need TPN feeding due to complex health conditions that keep their digestive tract from functioning correctly. Such conditions include:
- Cancer
- Crohn’s disease
- Intestinal failure
- Ulcerative colitis
- Bowel obstruction
- Severe pancreatitis
- Short bowel syndrome or ischemic bowel disease
Anyone who can’t receive enough calories through their gastrointestinal tract can qualify for TPN therapy.
This therapy may be temporary for some patients, like those recovering from surgery. It can be provided at the hospital. For others, it may be a lifelong treatment. These patients can receive their infusions at home from certified nurses or even perform it themselves.
TPN for Teens and Children
TPN treatments are also common among children and teenagers. Many of the younger candidates receiving this therapy have short bowel syndrome or other intestinal ailments. Some of those receiving TPN may also be on waiting lists for intestinal transplants.
However, adjusting to a life with TPN is much more difficult when you are younger. Teenagers receiving TPN therapy are generally more concerned with their body image, and treatment could affect their self-confidence. They may even decide to stop their TPN early or refuse treatment.
With pediatric patients, it is recommended to reach out to support groups and professionals. There are numerous non-profit organizations available to help families with children on TPN.
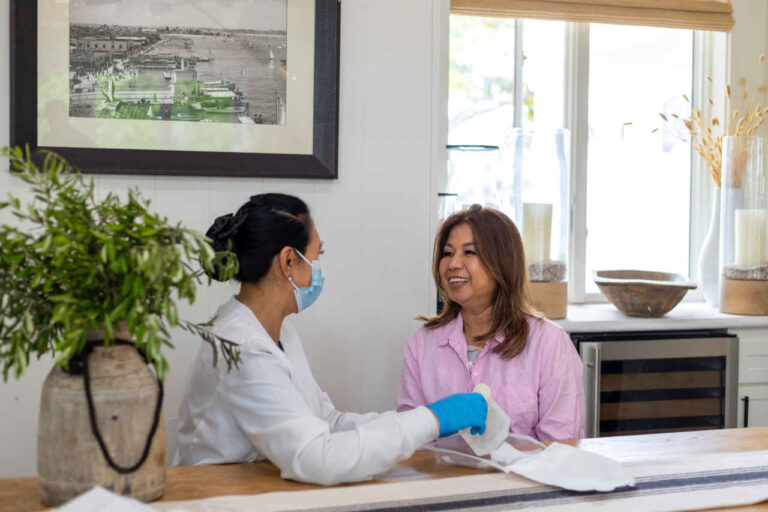
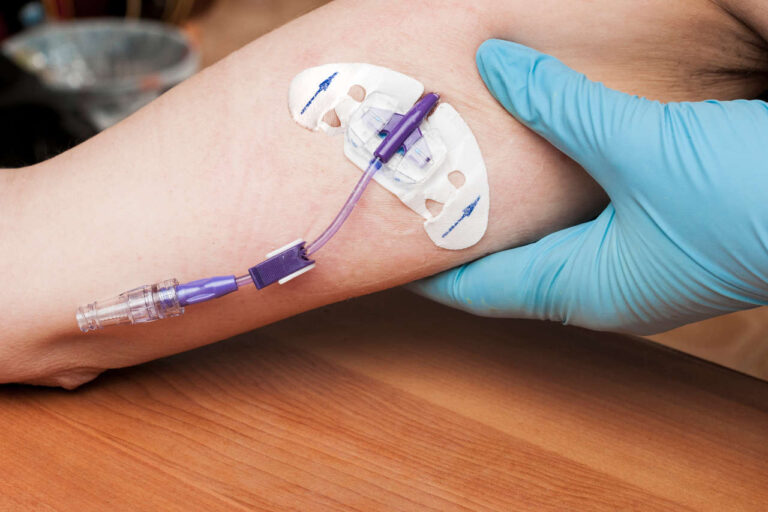
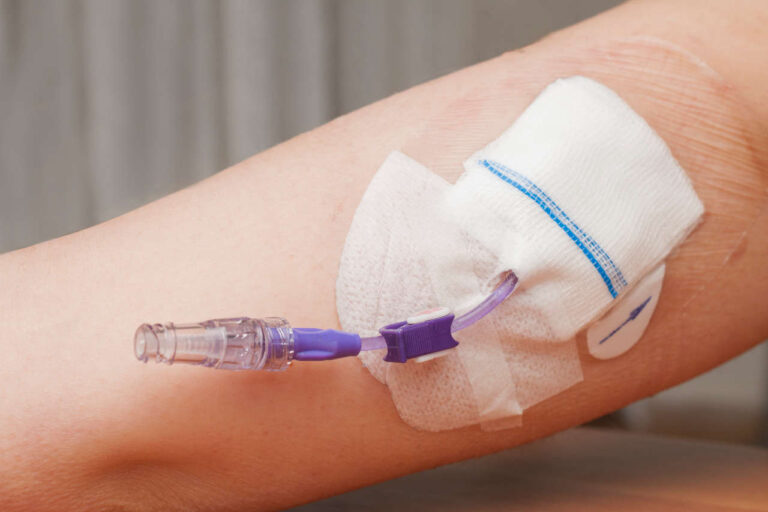
TPN Administration

The administration of TPN is similar to any other IV therapy. The TPN formula is provided as a liquid solution inside a bag. A trained nurse will prepare the treatment and connect the infusion tubing to a catheter. Finally, the nutrients will enter your vein during a continuous infusion.
TPN therapy can run for 10 to 24 hours. The duration of daily infusions may shorten after several sessions. Most patients opt to receive their TPN treatments at night while asleep. This process can be done at home or in a hospital.
Whenever prepping for your infusion, sterile techniques must be used to prevent infections. Dressings are changed weekly by a nurse and external tubing replaced daily to avoid infection complications.
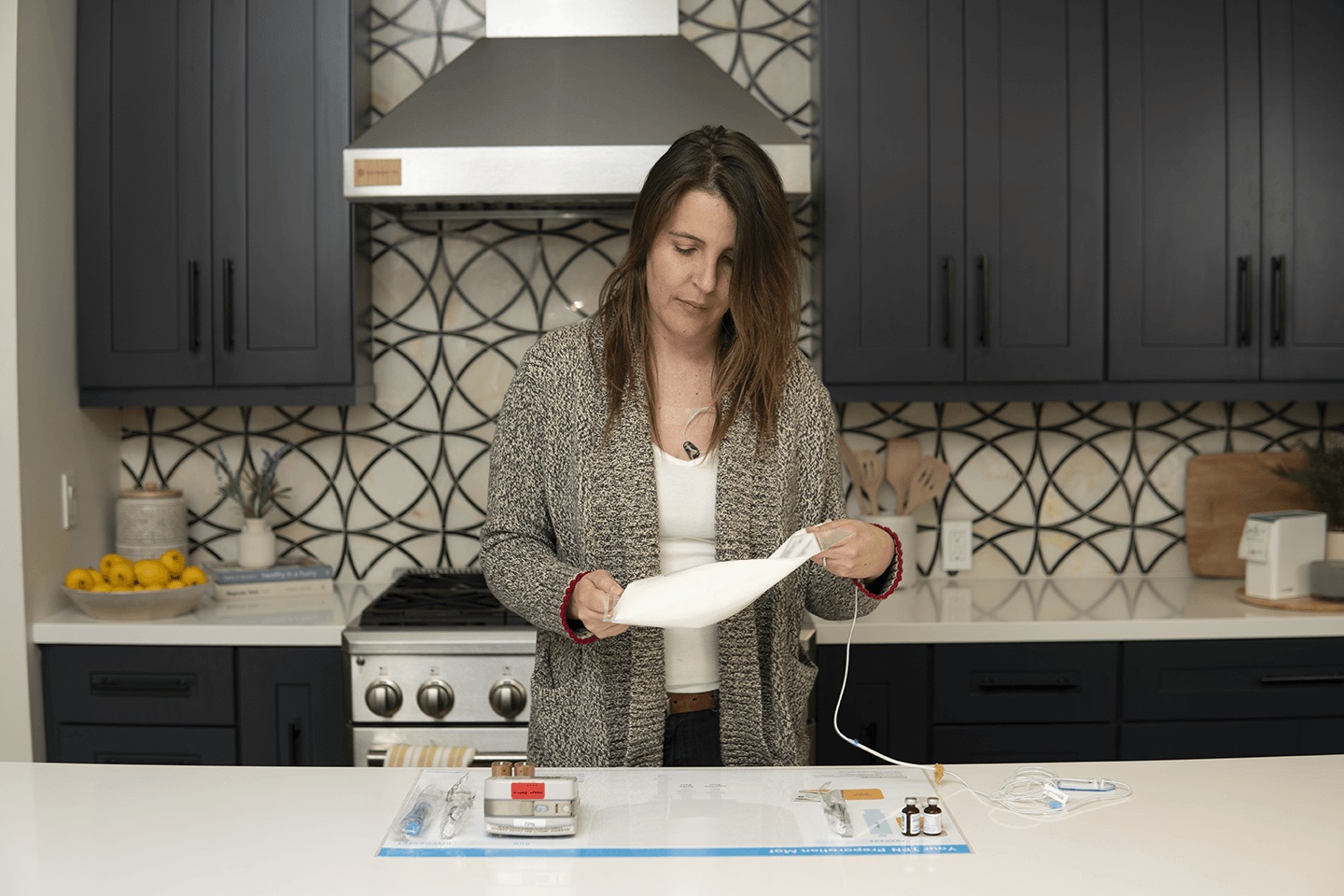
Administering TPN At Home
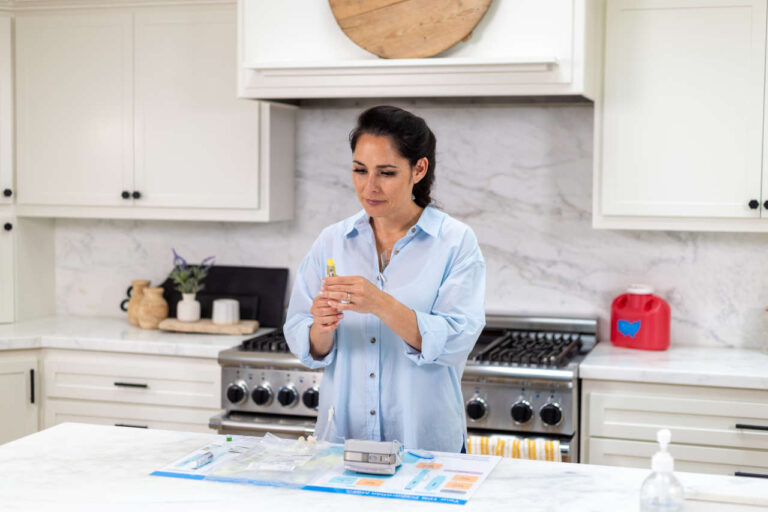
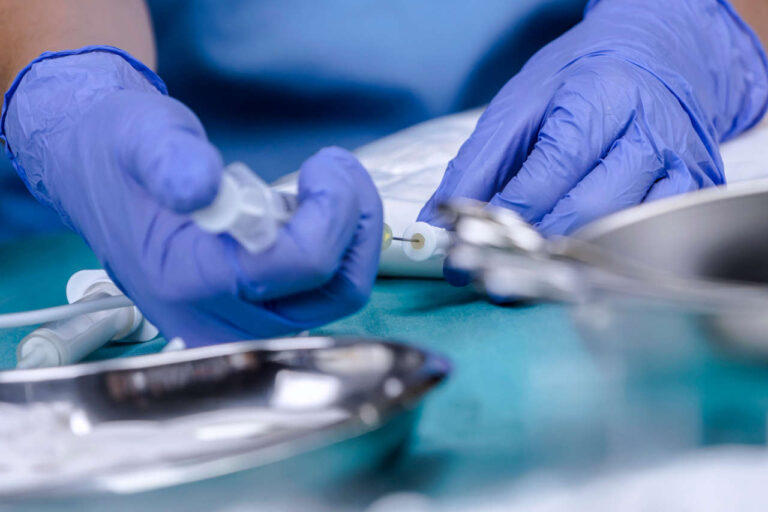
Alternatively, you can administer TPN yourself. Administering TPN therapy is safe and easy if you follow some guidelines and perform the treatment in a clean environment. Here is a step-by-step guide to administering TPN yourself.
Step 1: Prepare a Sterile Environment
The first step is to prepare a hygienic environment to prevent infections. You can do this by disinfecting the area where you want to put your equipment and washing your hands with an antibacterial soap. Also, wash the TPN treatment area with soap and water and pat it dry with a clean towel.
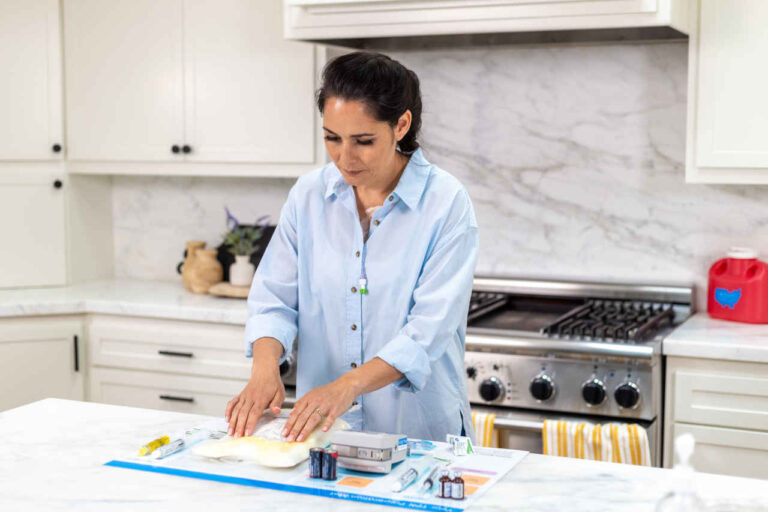
Step 2: Prepare the TPN Bag
Take your TPN bag out of the fridge and inspect it thoroughly before starting your TPN therapy. Ensure it has the right ingredients and is not expired. The color should be consistent without any visible fat particles or cloudiness.
Place it on a clean paper towel and let it rest for two to three hours until it reaches room temperature. Continuing treatment with a cold formula may give you headaches and make you uncomfortable.
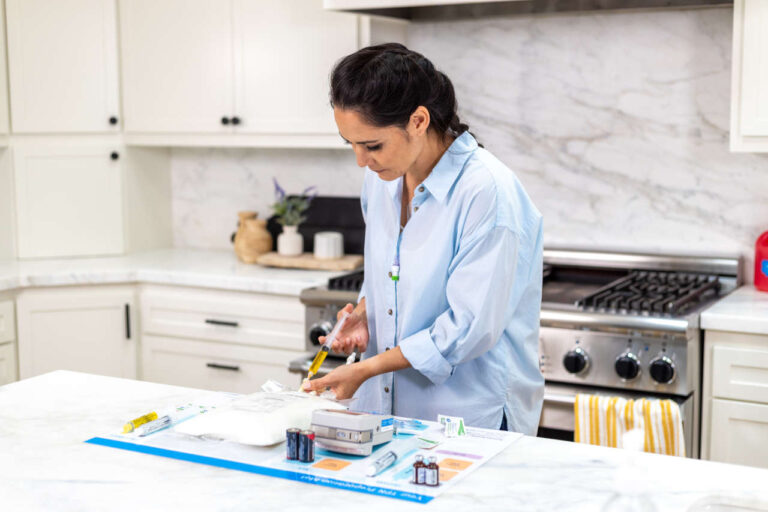
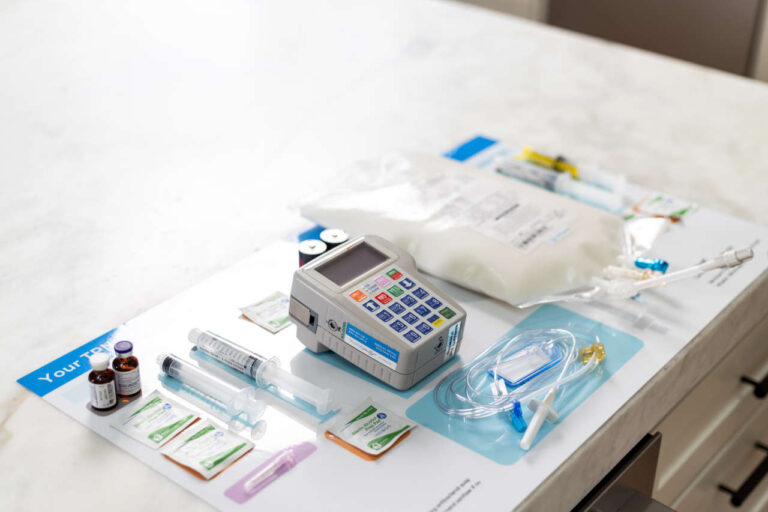
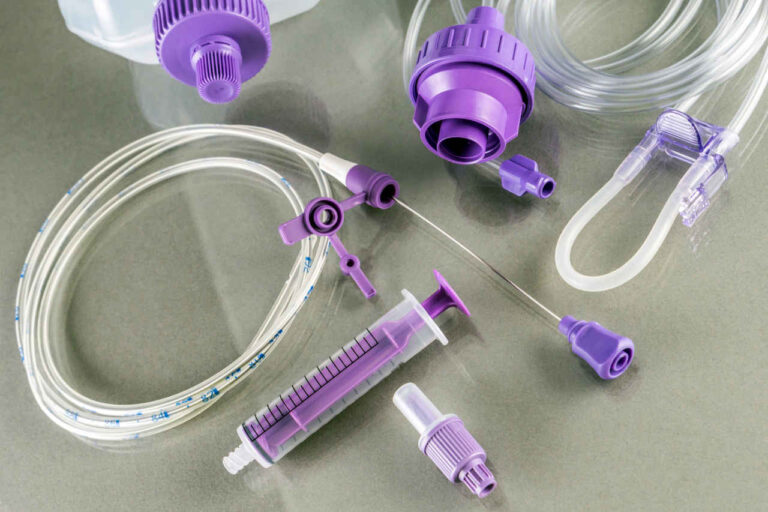
Step 3: Gather Your Supplies
Gather all the necessary TPN equipment and place them in a sterile area to perform the infusion. Here is a list of supplies you will need:
- Syringes
- Prescribed multivitamins
- Medical gloves
- Antiseptic caps
- IV tubing
- Infusion pump
- Alcohol wipes
- Prefilled saline and heparin syringes
- Sharps disposal container
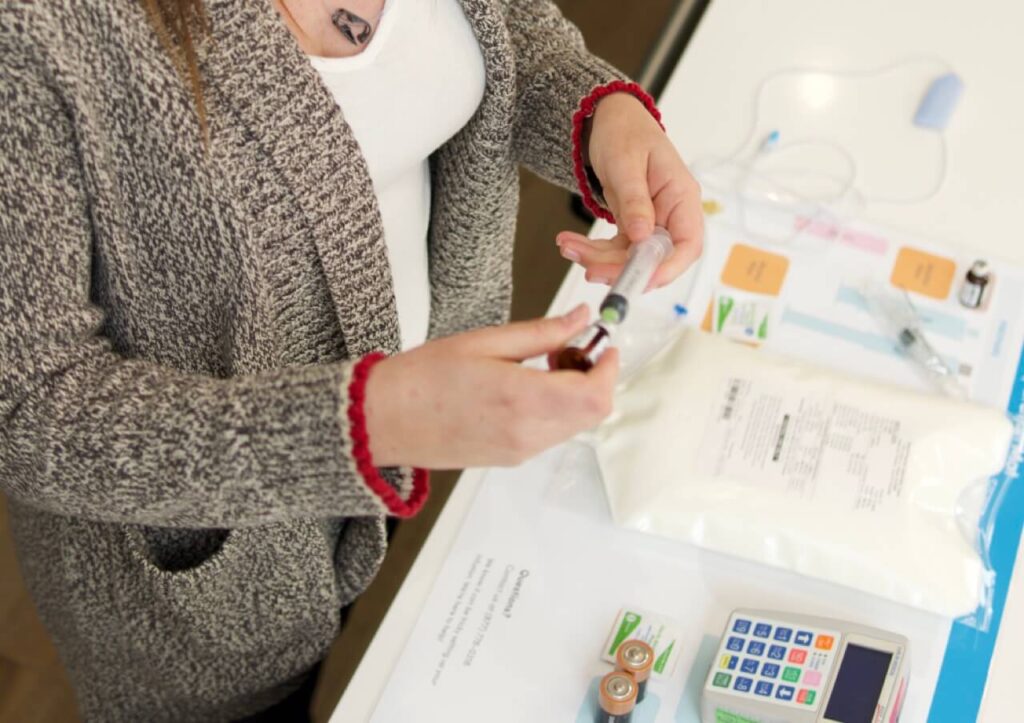
Step 4: Add the Multivitamins to the TPN Bag
If your doctor has prescribed you multivitamins, you must add them to the bag before starting your TPN therapy. Check the labels to ensure they’re the right ones and not expired. Draw the solutions into a syringe and empty the contents into the TPN bag.
Step 5: Prime IV Tubing
Before you begin TPN treatment, you need to prime the IV tubing. Priming is the process of transferring the contents of the TPN bag to the IV tube line using a pump.
All you have to do is attach one end of the tube to the TPN bag. Turn on the attached pump, select the prime tubing feature, and wait for the solution to fill the IV tube.
Step 6: Flush the Central Line
Before your TPN therapy, you need to flush the central line of the catheter to remove residual medications from previous infusions. Insert a saline syringe into the catheter cap and rinse the line. Discard the used syringe afterward.
Step 7: Start the Infusion
Connect the other end of the IV tubing to your catheter. Secure the connection and start the pump for the TPN formula to enter your body.
Step 8: Disconnect the IV Tubing
When the infusion is complete, the pump will alert you. Turn off the device and carefully disconnect the tube from the catheter.
Step 9: Flush the Central Line
After completing the TPN therapy, you must flush the central line again with saline and a heparin solution. Follow the instructions in step 6.
Step 10: Secure the Central Line and Discard the Supplies
After your TPN treatment is complete, secure the central line and sterilize the injection port of the catheter with an alcohol wipe. Dispose of all the used supplies. Throw the syringes with the attached needle into the sharps container and the TPN bag in a trash bag.
Benefits of TPN
TPN therapy offers numerous benefits by nourishing your body with the necessary nutrients. Some benefits include the following:
- Providing hydration
- Increasing strength levels
- Maintaining high energy levels
- Enabling patients to heal more quickly
Apart from these benefits, TPN is helpful for children and teenagers as it provides them with the nutrients they need to avoid growth delays.
Side Effects of TPN
TPN is not risk-free. As with any other medical treatment, it has minor risks that some patients may experience. Some of TPN’s side effects include:
- Blood clots
- Bone disease
- Liver dysfunction
- Nutrient imbalance
- Catheter infections and sepsis
- Glucose abnormalities, including hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia
Catheter-related infections are the most common side effects. Meanwhile, liver dysfunction and bone disease are more prevalent in long-term patients. You can lower the risk of most of these side effects by receiving TPN therapy under the supervision of a licensed professional in a clean environment.
Receive Professional TPN Treatment With AmeriPharma™ Specialty Pharmacy
You can receive your daily dose of nutrients from certified nurses at AmeriPharma™ Specialty Pharmacy. We offer convenient home infusion treatments and TPN services to those who are unable to get their nutrients through diet.
Our URAC-accredited specialty care pharmacy operates in over 40 U.S. states. We make life with TPN treatment easier with full-service coordination, including copay assistance and 24/7 support. Contact us now to speak to an infusion specialist and get started with your TPN therapy.
Visit our blog to learn more about TPN infusions and other treatments for complex health conditions.