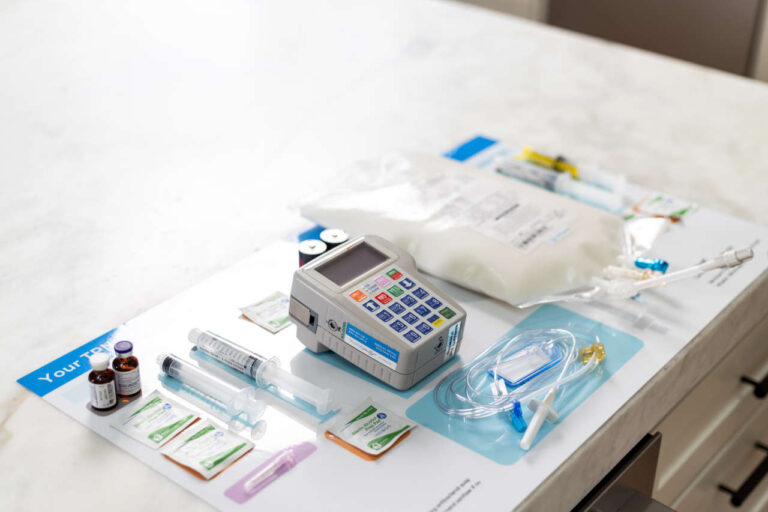
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) can be lifesaving or life-sustaining, but it is not risk-free. There are several risks of TPN, such as catheter infections, high or low blood sugar levels, fatty liver, gallstones, and brittle bones.
Get Financial Assistance for TPN
Total parenteral nutrition uses a special formula—administered through a vein—to fulfill all your daily nutritional needs.
It may be the only option in the following cases:
- Certain stages of ulcerative colitis
- Bowel obstruction
- Babies born with digestive tract anomalies
- Shortened small bowel following surgery
Unlike enteral nutrition, TPN is not associated with higher death rates or prolonged hospitalization [1]. However, several potentially serious complications can occur, especially among those on prolonged parenteral nutrition.
Fortunately, your nutritional support team can help reduce the risk of TPN side effects.
What Are the Common Risks of TPN?
The type and severity of TPN complications can vary depending on:
- Patient factors, such as nutritional deficiencies, underlying illnesses, and use of other medicines
- The type of TPN (long-term vs. short-term)
- The proportions of nutrients in the TPN formula
- The infusion rate
1. High or low blood sugar levels
Blood sugar imbalances are the most common risk of TPN.
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, occurs in up to 50% of individuals on TPN [1]. On the other hand, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, is more likely to occur if individuals are receiving insulin therapy.
Rebound hypoglycemia may occur when you suddenly stop TPN. However, this is rare.
For optimal blood sugar, your nutritional support team will give you calculated doses of insulin and dextrose.
2. Catheter-related complications
Catheter-related complications occur more frequently with long-term TPN and include:
- Catheter sepsis: A medical emergency in which blood infection due to bacteria from the catheter causes your immune system to overreact.
- Occlusion of the central venous catheter: Improper flushing of the catheter or precipitation of certain components of the TPN formula can block the catheter.
- Blood clots: Blood clots may form in the area where the catheter and vein meet.
3. Liver problems
TPN-associated liver problems include:
- Fatty liver: The most common liver problem in which fat accumulates in your liver
- Cholecystitis: The swelling of the gallbladder
- Cholelithiasis: The presence of gallstones

4. Metabolic bone diseases
Metabolic bone diseases are one of the metabolic complications of TPN, commonly affecting those on long-term TPN (longer than 3 months).
Examples include brittle bones (osteoporosis) and soft bones (osteomalacia).
5. Elevated triglyceride levels (hypertriglyceridemia)
Up to 50% of individuals on TPN get hypertriglyceridemia. Extremely high blood levels of triglycerides increase the risk of acute pancreatitis (sudden, transient inflammation of the pancreas).
AmeriPharma™ Specialty Care | Total Parenteral Nutrition
Leader In TPN Assistance6. Refeeding syndrome
Refeeding syndrome can occur when a severely malnourished person on aggressive TPN starts feeding again. Symptoms can include:
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty breathing
- Double vision
- Seizures
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of memory
- Low blood pressure
- Frequent urination
To prevent refeeding syndrome, your healthcare team will regularly monitor your blood sugar and heart function during TPN feeding.
Risks of TPN: Frequently Asked Questions
What are the medical contraindications for TPN?
- Infants with short small intestines (less than 8 cm)
- Individuals with severe, irreversible brain damage
- Individuals with unstable heart function or metabolic function
- Individuals for whom other methods of feeding are possible
Does TPN increase the risk of infection?
TPN can increase the risk of a central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI).
What is the most common complication of TPN?
Blood glucose imbalances (hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia) and liver problems are the most common complications of TPN.
REFERENCES:
- Hartl, W H et al. “Complications and monitoring – Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition, Chapter 11.” German medical science: GMS e-journal vol. 7 Doc17. 18 Nov. 2009, doi:10.3205/000076