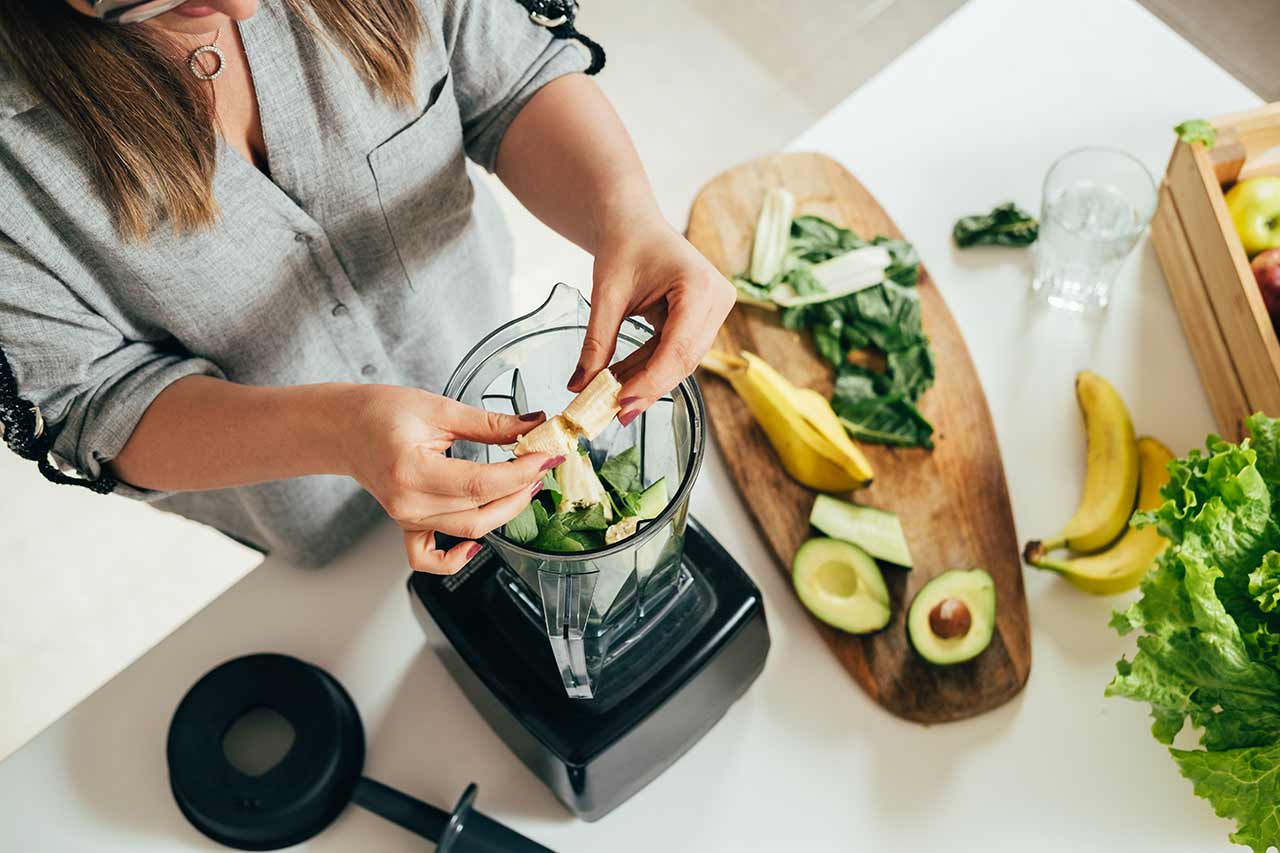
Diet combined with a healthy lifestyle undoubtedly makes a significant impact on your health regardless of the type of hemophilia you have. Although there is no cure for this life-threatening bleeding disorder, you can still live a near-normal life by making proper dietary choices.
Get IVIG Copay Assistance
Speak to a SpecialistThough there is currently no evidence-based data in humans to determine which diet is best for people with hemophilia, following a nutrient-dense diet will strengthen your body so that you experience fewer bleeding complications. A nutrient-dense diet will also help you maintain a better quality of life.
On the other hand, unhealthy lifestyles and poor dietary choices increase the risk of obesity in hemophilia patients. The extra pounds you gain from being obese can strain your weight-bearing joints and increase the risks of internal bleeding in vulnerable areas. As a result, this also accelerates your course of treatment.
Because of these reasons, maintaining a healthy weight along with a healthy diet is of utmost importance for hemophilia patients.
Role of Diet in Hemophilia
In general, people with hemophilia bleed longer than normal individuals due to a deficiency of blood clotting proteins. Therefore, it is important for hemophilia patients to replace blood loss and maintain an average blood volume in their bodies through a good diet.
Diet provides essential nutrients such as protein, copper, iron, folic acid, vitamin K, B12, B6, and vitamin C, which are all important for red blood cell (RBC) production. Diet can also help you maintain a continuous and healthy blood supply in the body.
Below are the lists of essential nutrients that you or your caregiver should add to your diet while planning or making your food:
Foods Rich in Iron

Eating foods rich in iron is beneficial for hemophilia patients. Iron helps in the formation of red blood cells, and its protein called hemoglobin (an iron-rich protein responsible for transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body).
In fact, RBCs account for about 70% of the body’s iron, and you are more likely to lose iron during bleeding episodes. It has been estimated that 0.75 mg of iron is lost with each 15 ml of blood.
To replenish the iron and increase RBC production in your body, you must add iron-rich foods to your diet.
Iron-rich food sources include animal proteins such as lean red meat, liver (a good source of clotting factors as well), seafood and poultry, dark leafy greens, legumes, seeds, peas, fortified grains, specific vegetables and fruit, and specific spices and herbs. Vitamin C can help boost iron absorption, so it is helpful to increase variety on your plate, such as having spinach with poultry or having fruit as a side or for dessert.
Vitamin K-Rich Foods
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting. This fat-soluble vitamin helps in the production of one of the blood clotting factors called prothrombin (a blood clotting protein). Adding vitamin K-rich foods would benefit people with hemophilia and help control their excessive bleeding episodes.
Vitamin K-rich foods include plant and animal sources such as:
- Leafy greens (e.g., kale, Swiss chard, mustard greens, asparagus, broccoli, and spinach)
- Cabbage
- Green tea
- Canola
- Oats
- Olive oil
- Alfalfa
- Bran
- Natto
- Nuts
- Legumes
- Full fat dairy
- Chicken
- Pork chops
- Beef liver
Can IVIG help?
Free IVIG Treatment InfoFoods Rich in Vitamin B and C
Vitamin B6 and B12 help in the production of RBCs, while vitamin C helps in iron absorption, improves the blood clotting process, and helps collagen production. A good amount of collagen in your body can reduce the severity of bruising if you have hemophilia.
Examples of foods rich in vitamin B6 include chickpeas, tuna, salmon, chicken breast, turkey, and fortified breakfast cereals.
Foods rich in vitamin B12 include beef liver, clams, oysters, nutritional yeast, salmon, and tuna.
Examples of foods rich in vitamin C include oranges, pineapples, kiwis, strawberries, lemons, blueberries, tomatoes, and broccoli.
Calcium-Rich Foods
Calcium is an important mineral that is required by your body to build strong bones. Hemophilia patients experience poor bone health due to joint bleeding. Therefore, adding a good source of calcium to your daily diet will help you to withstand future joint complications. Examples of calcium-rich foods include dairy products, leafy greens, fortified foods such as soy or almond milk, and specific types of beans and seafood. Calcium and Vitamin D have a close relationship, so eating foods that have both can boost calcium absorption, such as dairy and salmon, or increasing the variety on your plate to include calcium and vitamin D-rich food sources.
Conclusion
Eating a nutritious diet and maintaining a healthy weight can effectively ease your symptoms and complications related to hemophilia. Additionally, if you are struggling with cardiometabolic issues, research has shown that adolescents who adhered to the DASH eating pattern saw improvements in blood cholesterol, blood pressure, and blood sugar.
It is recommended that you consult your licensed healthcare provider to make a personalized diet plan.
REFERENCES:
- Abbaspour, N., Hurrell, R., & Kelishadi, R. (2014). Review on iron and its importance for human health. Journal of research in medical sciences: the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 19(2), 164.
- Mahmood, L. (2014). The metabolic processes of folic acid and Vitamin B12 deficiency. Journal of Health Research and Reviews, 1(1), 5. https://www.jhrr.org/article.asp?issn=2394-2010;year=2014;volume=1;issue=1;spage=5;epage=9;aulast=Mahmood