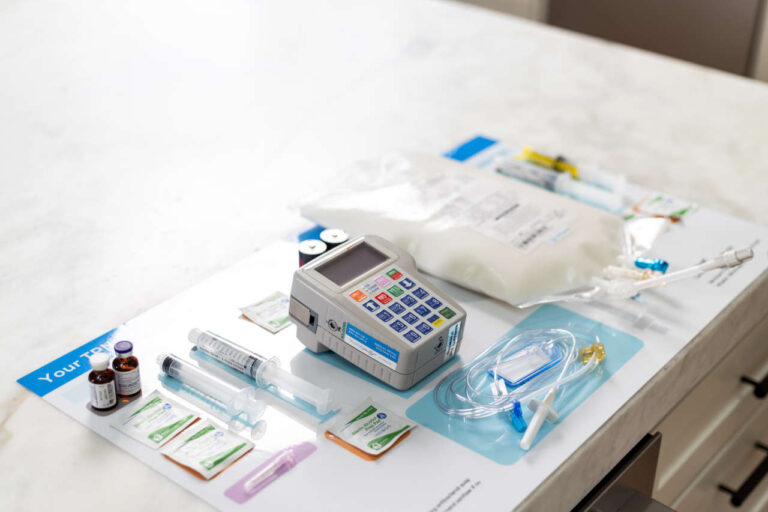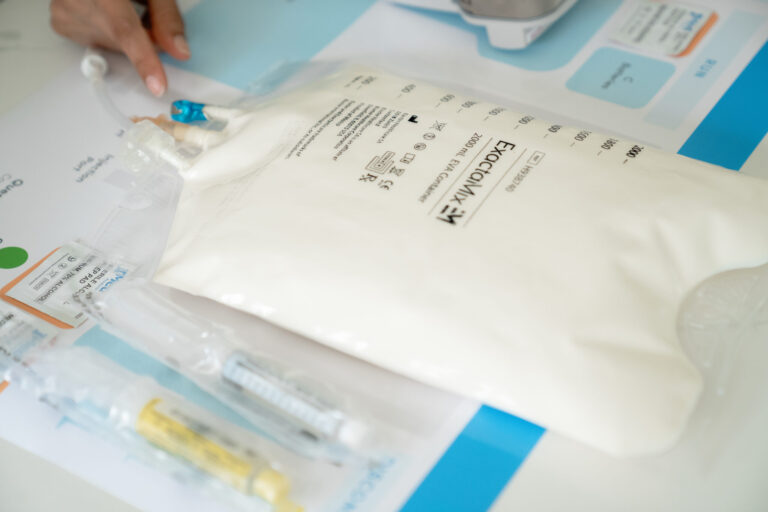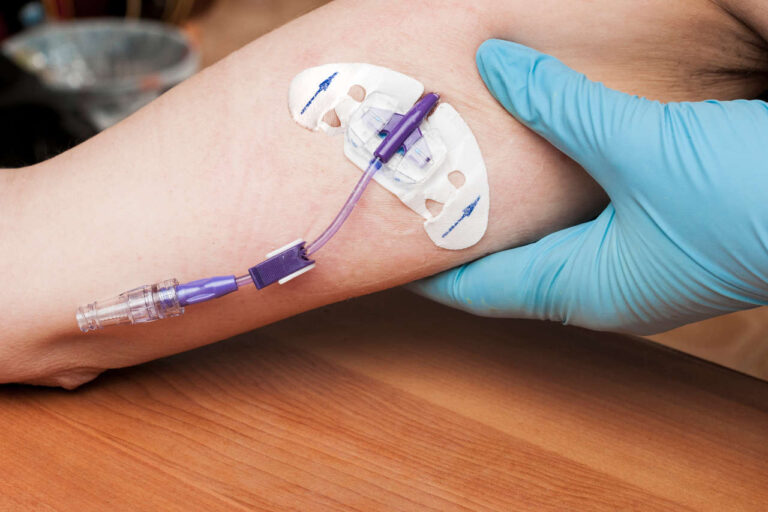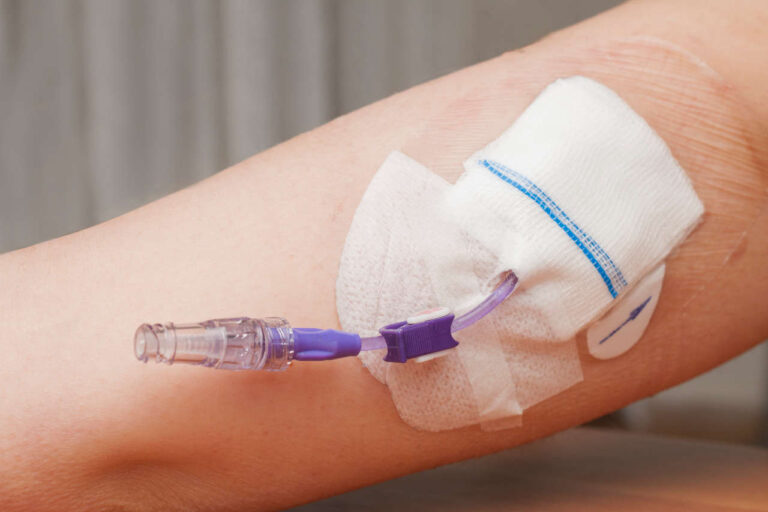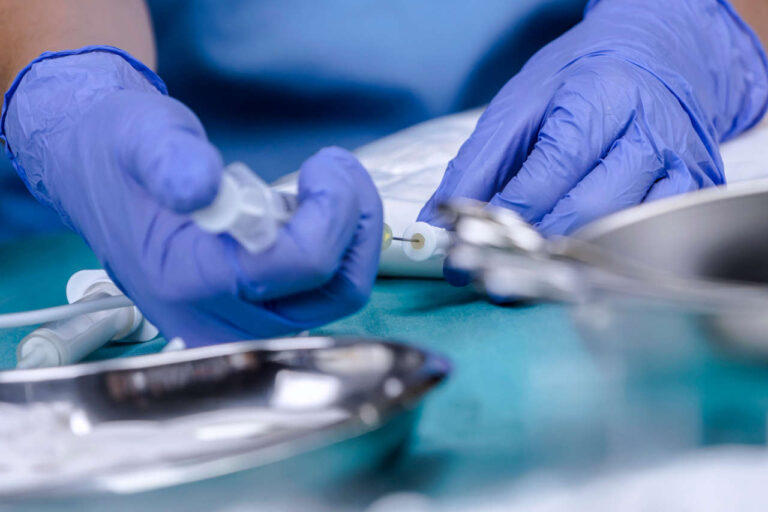
TPN is a life-saving treatment for many patients who can’t consume food or drink by mouth. It allows them to receive the necessary nutrients the body needs to stay healthy and function properly. However, there’s a risk of complications, including central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI).
Always in Stock
Full inventory of IV fluids, ready for youCLABSI in patients receiving TPN can lead to prolonged hospital stays, higher healthcare costs, and even death. In fact, over 28,000 patients die from this complication annually. However, preventing CLABSI with TPN is possible and easy.
This guide will show you how to prevent CLABSI with TPN by following proper guidelines and central line maintenance techniques.
Understanding TPN Therapy
Total parenteral nutrition, or TPN therapy, is a form of intravenous nutrition therapy that provides patients who can’t consume food or drink by mouth with all the essential nutrients their body needs to function.
Providers may prescribe TPN for cancer patients and those with gastrointestinal disorders, short bowel syndrome, recovering from surgery, among others.
TPN typically includes micronutrients (e.g., minerals, vitamins, electrolytes), and macronutrients (e.g., proteins, fats, and carbohydrates). The patient’s health condition and blood test values will determine what’s in a TPN solution.
Healthcare professionals should know the contents of the solution to prevent CLABSI with TPN effectively.
Administering TPN
TPN can be administered through a central venous access device (CVAD) or a peripheral intravenous catheter.
After selecting the insertion site, nurses will attach the CVAD, prepare the solution, take the necessary measures to prevent CLABSI with TPN, and administer the solution. The nutrients will enter the patient’s bloodstream and support their vital functions.
Complications of TPN
TPN is associated with various complications. Metabolic complications of TPN include conditions like hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), electrolyte imbalance, refeeding syndrome, and liver dysfunction.
There is also the risk of non-metabolic complications that can be just as dangerous. One of these complications is CLABSI, and knowing how to prevent CLABSI with TPN can be the difference between life and death for a patient.
What Is CLABSI?
CLABSI, or central line-associated bloodstream infection, is when harmful pathogens like bacteria enter the patient’s bloodstream through a central line or catheter.
While this TPN complication can be a potentially life-threatening infection, you can easily prevent CLABSI with TPN.
Risk Factors for CLABSI in Patients Receiving TPN
Several risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing CLABSI while receiving TPN include:
- Poor catheter care
- Long hospital stays
- Weakened immune system
- Prolonged need for vascular access
- Limited access sites for central lines
- Improper aseptic technique during TPN administration
- Underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or cancer
- Concurrent use of other invasive devices, such as urinary catheters
Tips to Prevent CLABSI with TPN

Healthcare providers must implement the best practice recommendations during treatment administration to prevent CLABSI with TPN. Here are some measures you can take to reduce the risk of CLABSI:
Selection of Appropriate Devices
The first step to preventing CLABSI involves choosing the appropriate devices for TPN therapy. Healthcare professionals must assess each patient’s medical history and determine their needs based on their current symptoms.
They must assess the potential health risks associated with different types of central venous access devices and select the best one, depending on the potential for complications and the patient’s duration of therapy.
Site Selection
The second factor to consider to prevent CLABSI with TPN is to select a proper site for CVAD insertion. To determine the best site, assess the patient’s activity level, age, and the size of the CVAD.
The best practice is to choose the non-dominant side of the patient’s body for CVAD insertion. Choosing this side will reduce the risk of contamination from the patient’s hand and make them more comfortable.
Selecting the appropriate site can also reduce the risk of accidental dislodgement of the device and prevent complications such as hematoma, skin necrosis, and vascular damage.
AmeriPharma Specialty Care
Total Parenteral Nutrition | Leader In TPN Assistance
Proper TPN Solution Preparation
The next factor that will help you prevent CLABSI with TPN is how you prepare the solution to infuse into the patient’s bloodstream. To prevent CLABSI with TPN, you must follow the hygiene protocols from the first step.
This means preparing the TPN solution in a sterile environment, following the recommended aseptic techniques and strict personal hygiene protocols. Using in-line filters is another step that can remove the pathogens from the solution and reduce the risk of infection.
Correct Insertion of the Catheter
A fundamental part of preventing CLABSI with TPN involves correct catheter insertion. Whether you’re in a hospital setting or provide home TPN therapy, you must follow strict aseptic protocols during catheter insertion.
Use the maximum barrier precautions (gloves, masks, caps, and gowns) and adhere to standard aesthetic practices. Before inserting the catheter, disinfect the patient’s skin with antiseptic swabs.
Ensure the catheter is in the subclavian vein, not the femoral or internal jugular veins. These veins are associated with higher infection rates. Don’t forget to hold tension on the catheter while inserting the CVAD.
Regular Catheter Care and Line Maintenance
The most critical step for preventing CLABSI with TPN involves proper care and maintenance of central venous catheters.
If you want to learn how to prevent CLABSI with TPN by properly maintaining the line integrity, here are some measures you can take.
Change Line Dressings Routinely
The risk of CLABSI depends heavily on how often you change TPN tubing and dressing. Routine dressing changes are necessary for reducing the risk of contamination and infection.
You must change the dressing every seven days or sooner. Schedule changes according to the dressing type and the patient’s needs.
Change the dressing in a sterile environment to minimize the risk of infection and prevent CLABSI with TPN. In addition, flush the catheter regularly with heparin or sterile saline to prevent blockages.
Inspect for Signs of Infection
Inspect the line daily for signs of infection, dislodgment, and blockage. If there are any signs of these incidents, address the underlying problem immediately to avoid further complications.
Don’t Disconnect CVADs
Lastly, don’t disconnect CVADs unless you need to make a routine assessment, changing the dressing, or administering TPN.
If you disconnect the CVADs from the TPN equipment, you risk introducing pathogens into the solution. So, disconnect the line only when necessary to prevent CLABSI with TPN.
CLABSI Detection

You must know the signs of CLABSI because early recognition and treatment can help the patient avoid potentially life-threatening complications.
If you notice any swelling, redness, fever, chills, or hypotension, the patient is most likely infected.
Obtain blood cultures to determine the best course of antibiotics and start treatment immediately.
Education and Training
It’s essential that both healthcare professionals and patients are educated on ways to prevent CLABSI with TPN as well as CLABSI symptoms to watch out for.
Healthcare providers must receive ongoing education to learn the best practices for inserting and maintaining central venous catheters.
Patients must also receive education on the symptoms of CLABSI, proper care of the CVAD, and steps to take if they suspect an infection.
Get Financial Assistance for TPN
Using Evidence-Based Guidelines
You must always use evidence-based guidelines and protocols if you want to learn how to prevent CLABSI with TPN effectively.
The most reliable TPN troubleshooting guides are regularly updated to reflect the latest current practices. By following these established guidelines, you can minimize the risk of infection, prevent CLABSI with TPN, improve patient outcomes, and ensure successful treatment.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Patients
Lastly, special considerations and protocols must be in place for patients at a higher risk of CLABSI.
For instance, people with compromised immune systems or underlying medical conditions are more prone to getting infected. So, they must receive TPN in more sterile environments and undergo more frequent catheter assessments.
These cautionary measures will ensure high-risk patients receive treatment without becoming infected.
Receive Safe TPN Therapy at Home from AmeriPharma® Specialty Pharmacy
Preventing CLABSI with TPN requires a comprehensive approach by healthcare professionals. They must know the latest protocols and implement the best practices to reduce the risk of infection. Otherwise, patients’ lives are at risk.
If you need TPN infusion therapy from reliable healthcare providers, AmeriPharma® Specialty Pharmacy can help. Our trained nurses know how to prevent CLABSI with TPN and ensure you receive your nutrients safely.
Our ACHC-accredited specialty pharmacy provides convenient treatments, copay assistance, and 24/7/365 support to those with complex medical conditions in 40+ U.S. states.
Contact us now to speak with a patient navigator and start receiving TPN treatments from the comfort of your home.