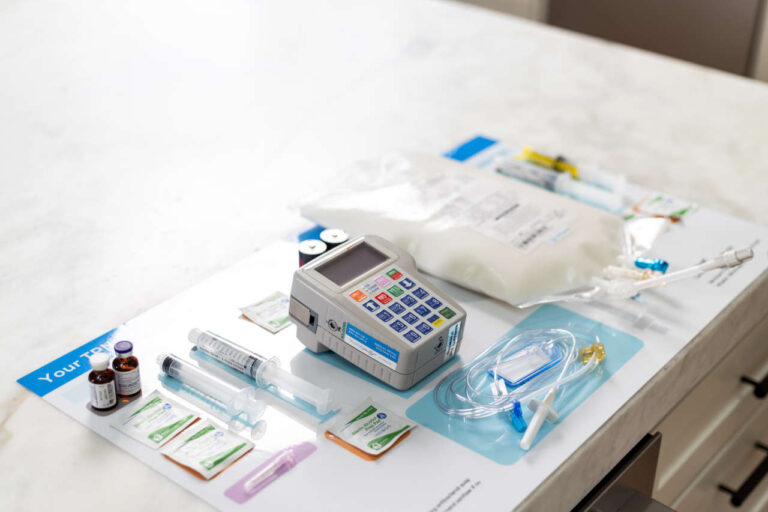
IV nutrition therapy, also called parenteral nutrition (PN), is the intravenous administration of nutrients directly into the bloodstream. Because there are medical conditions (acute and chronic) that prevent patients from receiving oral nutrition, intravenous nutritional therapies are needed in many cases. It is used in all age groups with a variety of indications. Patients can live well on PN therapy for as long as it is needed. Some may require therapy for a short time, while others will require therapy for a lifetime.
PN bypasses the normal digestion in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It is a sterile liquid formula given directly into the bloodstream through an intravenous (IV) catheter.
항상 재고 있음
귀하를 위해 준비된 IV 유체의 전체 재고Enteral Versus Parenteral Nutrition
Enteral nutrition (EN) is administered through a feeding tube placed into the stomach or intestines, whereas parenteral nutrition (PN) is administered through an IV line. PN therapy uses intravenous feedings when the GI tract is not usable (i.e., short-term after bowel resection surgery).
Both forms provide nutrition when the oral route is not available. EN is always preferred because it is the most physiological way to deliver nutrients when stomach function is preserved. The goal of EN is to use the gastrointestinal (GI) tract if and whenever possible. EN preserves GI and stomach function while being less costly compared to PN and is simpler to use. However, EN is associated with greater intestinal intolerance such as vomiting, reflux, and aspiration.
When EN is not possible, PN will be needed. PN is more complex and expensive but can be faster and more predictable. It is possible to dose with greater precision, and its effects are potentially immediate. However, PN does carry risks such as infection and metabolic abnormalities.
TPN vs. PPN
There are two subtypes of PN: peripheral parenteral nutrition (PPN) and total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Both types of PN provide nutrition to the body, with the key differences between the two being calorie content and treatment duration.
PN is for short-term use when the expected duration of treatment is no more than 2 weeks, usually during or after an acute event. Solutions are much more dilute and often meant to supplement nutritional needs rather than replace daily requirements. PN may be delivered through a peripheral vein (catheter that lasts for 3 – 4 days and is replaced as needed).
TPN, on the other hand, is much more comprehensive where the formula is calorie-dense and may replace the daily needs completely. It is often prescribed over PPN when the condition being treated is expected to be chronic with no definite timetable of recovery. TPN must be delivered through a central vein (catheter that lasts for weeks to months and is replaced as needed).
These types of therapies have evolved rapidly over the years and are safe and accessible. IV nutrition therapy is compounded as all-in-one admixtures where all necessary ingredients are sterile compounded into a single container by a pharmacy.
Speak to a Specialist about Copay Assistance
Ingredients in PN
The following are the ingredients found in PN:
- Protein (amino acids)
- Carbohydrates (dextrose)
- Fats (lipid emulsion)
- 전해질
- Trace elements
- Vitamins
- Other additives (e.g., insulin, folic acid) as clinically appropriate
PN is patient-specific where the above ingredients and amounts of each ingredient is personalized to meet the nutritional needs of the patient.
Indications for PN
The main clinical indications for PN include:
- Impaired absorption or loss of nutrients: Congenital bowel abnormalities, short bowel syndrome, complications of bariatric surgery, inflammation of the intestine from radiation (in cases of cancer)
- GI fistulas: Abnormal openings in the stomach or intestines that allow contents to leak
- Mechanical bowel obstruction: Partial or complete blockage in the intestines (i.e., strictures, inflammatory disease, cancer, ischemic bowel disease).
- Necessity to restrict oral intake (i.e., preoperative status or severe pancreatitis)
- Motility disorders (i.e., scleroderma or ileus [prolonged])
- Severe malnutrition, significant weight loss, or hypoproteinaemia when enteral therapy is not possible
Complications and Risks of PN
Possible complications associated with TPN include:
- Metabolic abnormalities
- Electrolyte imbalances — evaluated via weekly lab draw
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugars) — a concern with diabetic patients
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugars) — a risk with abrupt discontinuation of infusion, minimized by tapering infusion up/down at beginning/end of each infusion
- Thrombosis (blood clots)
- 전염병 — at the catheter site, sepsis (bloodstream infection)
- Liver dysfunction — evaluated via weekly lab draw
- Osteoporosis (bone disease) — a concern with long-term use of PN
- Edema — swelling from fluid overload, evaluated for weight gain and symptoms of edema (shortness of breath, frequent urination)
Ask About TPN At-Home Infusion
Interdisciplinary Healthcare Team
Because of the complexity of IV nutrition, an interdisciplinary healthcare team is required to manage TPN therapy. The team would include:
- A prescriber (MD, DO) – writes the order after deciding on the appropriate course of treatment and the type of nutrition. Collaborates with the patient’s primary health care team to ensure coordination of care.
- A dietician (RD) — conducts ongoing assessments of the patient’s nutritional status and calculates nutritional requirements.
- A pharmacist (PharmD/RPh) — processes and provides sterile IV nutrition. In addition, under the direction of the prescriber, a pharmacist may make reasonable adjustments to the TPN formula based on clinical assessments and laboratory results. A pharmacist will also collaborate with the dietician to optimize the patient’s formula to meet their nutritional needs.
- An infusion nurse (RN) — educates and trains the patient or caregiver on administration, pump use, and managing the TPN at home. An infusion nurse will also perform weekly lab draws and dressing changes.
Eating While Receiving IV Nutrition
Depending on the condition and diagnosis, a patient may be able to consume food and beverages while receiving IV nutrition therapy. If it is a possibility, oral intake is often encouraged to help expedite discontinuation. However, this should be done cautiously under the direction of the prescriber or dietician.
참고문헌:
- ASPEN What is Nutrition Support Therapy?
https://www.nutritioncare.org/About_Clinical_Nutrition/What_is_Nutrition_Support_Therapy
Accessed on April 26, 2022. - Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
Accessed on April 29, 2022. - ASPEN Parenteral Nutrition Fact Sheet
https://www.nutritioncare.org/About_Clinical_Nutrition/What_is_Nutrition_Support_Therapy
Accessed on May 2, 2022. - Home Parenteral Nutrition
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/total-parenteral-nutrition/about/pac-20385081
Accessed on May 2, 2022. - Complications – Total Parenteral Nutrition
https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-treatments/t/total-parenteral-nutrition-therapy/complications.html.
Accessed on April 28, 2022.