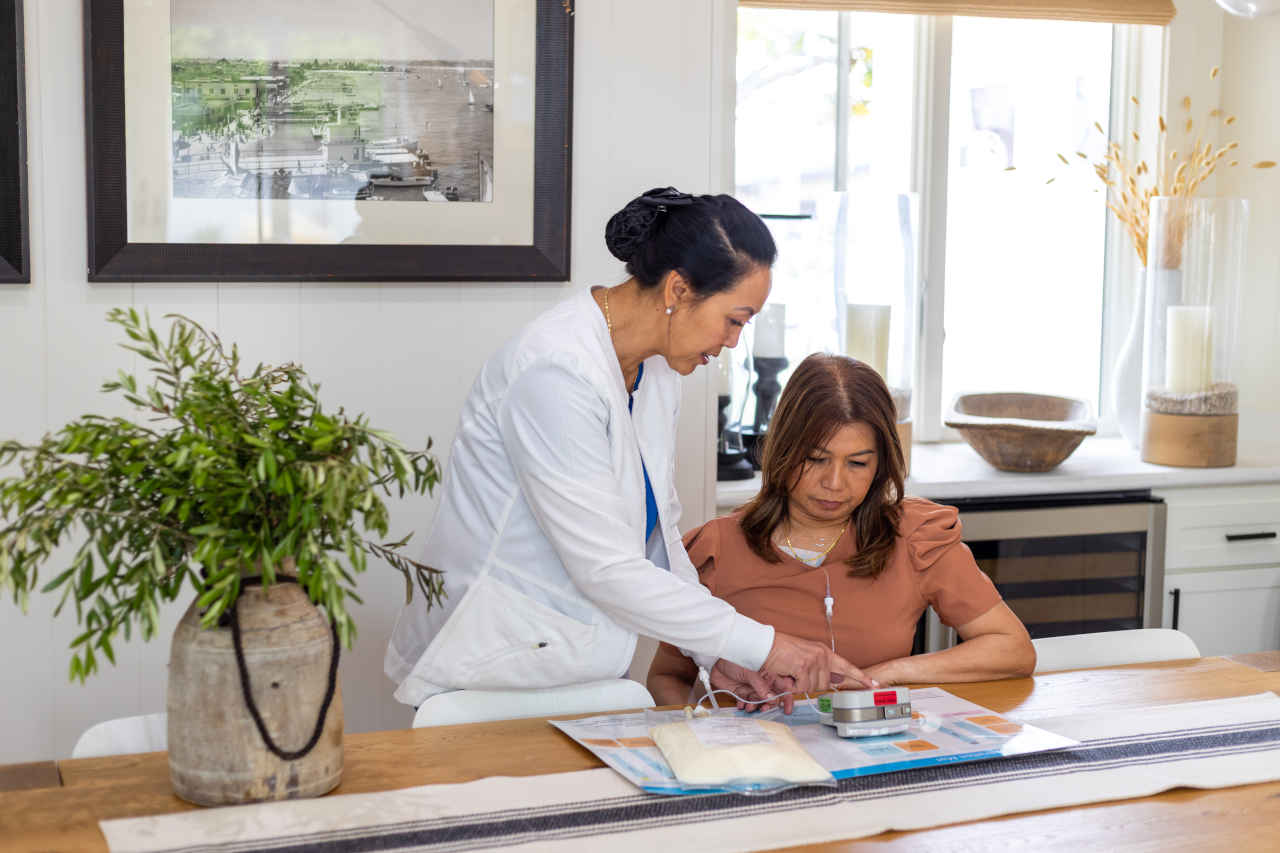
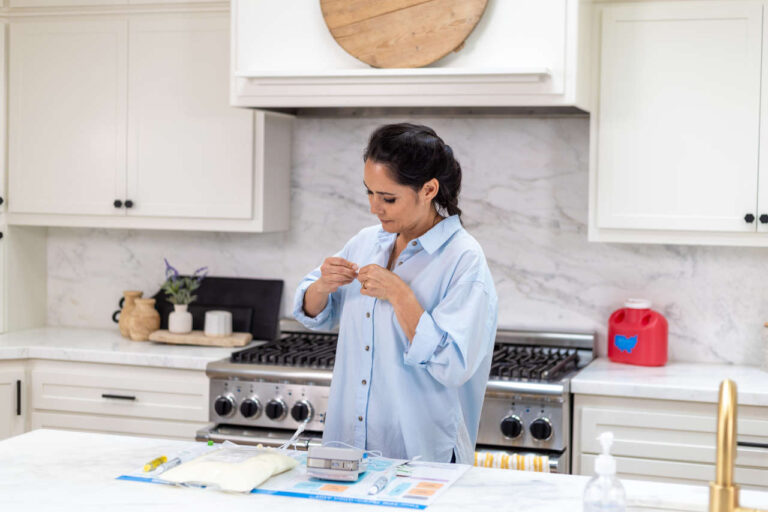
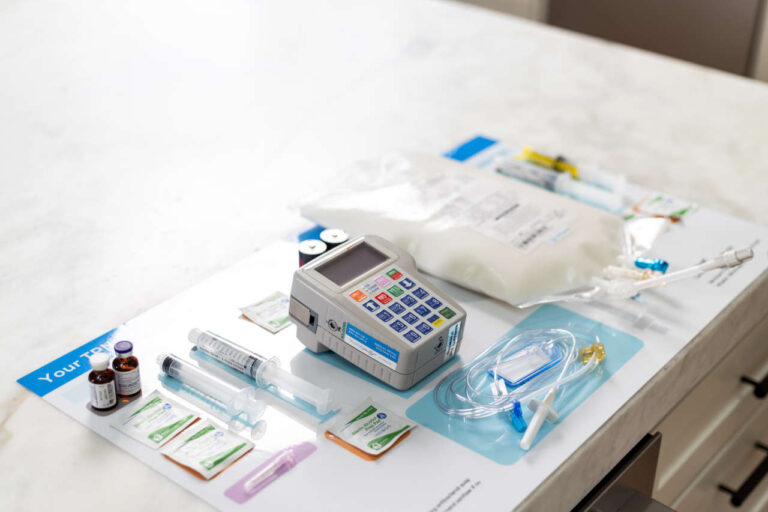
TPN, also known as total parenteral nutrition, is an intravenous drug therapy used for people with a compromised digestive system (gastrointestinal tract) or who are unable to consume food orally. TPN contains a mixture of various components to fulfill the nutritional or dietary needs of a person, including carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, minerals, and other trace elements.
IV Fluids Fully in Stock
Consistent availability, uninterrupted careUndoubtedly, TPN is a lifesaving therapy that delivers nutrients directly to the bloodstream. But as the method of food intake and the process of metabolism is suddenly changed through TPN, the body can exhibit some complications in response to change. TPN therapy should be used for the shortest duration possible and the switch to enteral (oral, feeding tube) therapy should be made as soon as a patient is able. In this blog, we will discuss the 4 most common metabolic complications that can arise with TPN, and how you can address or prevent them.
What Is Meant By Metabolic Complications and Why They Occur
Metabolism is the chemical reaction that takes place in our body to convert the nutrients present in our food into energy. When the normal metabolic pathway of our body is disturbed due to any reason, like during disease, treatment, drug therapy, or any other external factors, it may cause complications, which are commonly referred to as metabolic complications.
Metabolic complications commonly involve imbalances or disturbances in the levels of electrolytes, hormones, nutrients, and other substances that are needed for various bodily functions. These imbalances can lead to metabolic complications, like hyperglycemia, liver dysfunction, refeeding syndrome, and electrolyte imbalances.
Top 4 Metabolic Complications of TPN And How To Prevent Them
The 4 most common metabolic complications of TPN are:
Hyperglycemia (high blood glucose)
Total parenteral nutrition is commonly formulated according to the patient’s individual needs. As TPN solutions contain glucose, total parenteral formulations with higher amounts of glucose can increase the blood sugar levels of the patient, leading to hyperglycemia.
To prevent or reduce the risks of hyperglycemia, blood glucose monitoring during TPN therapy and the use of formulations with lower to moderate amounts of glucose are crucial. If hyperglycemia does occur from TPN use, it can be treated with certain medications, such as insulin, to reduce blood glucose levels. Additionally, careful monitoring of sugar levels is necessary for patients until complete recovery.
Electrolyte Imbalance
Another metabolic complication and major concern associated with TPN use is electrolyte imbalance. TPN administration can disturb the levels of electrolytes in the body, like calcium, sodium, magnesium, and potassium, which can lead to further complications, such as arrhythmias, neuromuscular dysfunction, and others.
The prevention of electrolyte imbalance requires close assessment of electrolyte levels, regular monitoring, and dose or formulation adjustments according to the patient’s condition with the collaboration of doctors, pharmacists, and nutritionists.
전문가와 상담하세요
공제금 지원에 관하여Refeeding Syndrome
Refeeding syndrome is a metabolic condition that occurs when a severely nutrient-deprived or malnourished patient receives excessive nutrition rapidly, like in TPN or other forms of dietary therapy. Refeeding syndrome causes electrolyte imbalances and vitamin deficiencies and can also lead to seizures, coma, or even death.
Hence, to prevent refeeding syndrome, it is crucial to adopt a gradual approach to nutritional therapy, mainly in severely nutrient-deprived or malnourished patients, as well as people who have undergone extreme dieting or starvation. Before administering TPN, the doctor or pharmacist must ask about the health history of the patient to prevent such occurrences from happening.
Liver Dysfunction
Liver dysfunction from TPN can occur as a result of fat (lipid) imbalance and excessive infusion of glucose or lipids, which can compromise the liver functions of the patient.
To reduce the risks of TPN-related liver dysfunction, healthcare providers minimize excessive administration and formulation of lipids and glucose in TPN therapy as well as carefully monitor liver levels to ensure no damage is being done. A switch to an enteral nutrition approach will help to decrease the risk of liver dysfunction in patients.