Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) can be difficult to diagnose, especially at its early stages due to its similarity in symptoms with other neurological diseases. Initial signs and symptoms can vary amongst each patient.
Physicians may conduct a physical examination of feet, limbs, and hands to check symptoms like numbness. They will indicate whether the symptoms appear on both sides of the body (which is a typical finding in GBS) and the speed at which the symptoms appear.
Get IVIG Copay Assistance – Speak to a Specialist
Key diagnostic testing includes:
1. Physical Exam
This is commonly the initial step to diagnosing GBS and checking the symptoms of Guillain-Barre syndrome. Physicians will generally look for the following symptoms:
- Recent onset, within days to at most 4 weeks of weakness occurring on both sides of the body, usually starting in the legs.
- Abnormal sensations such as numbness, pain, and tingling in the feet. These sensations can accompany or occur prior to weakness.
- Deep tendon reflexes are absent or diminished in weak limbs.
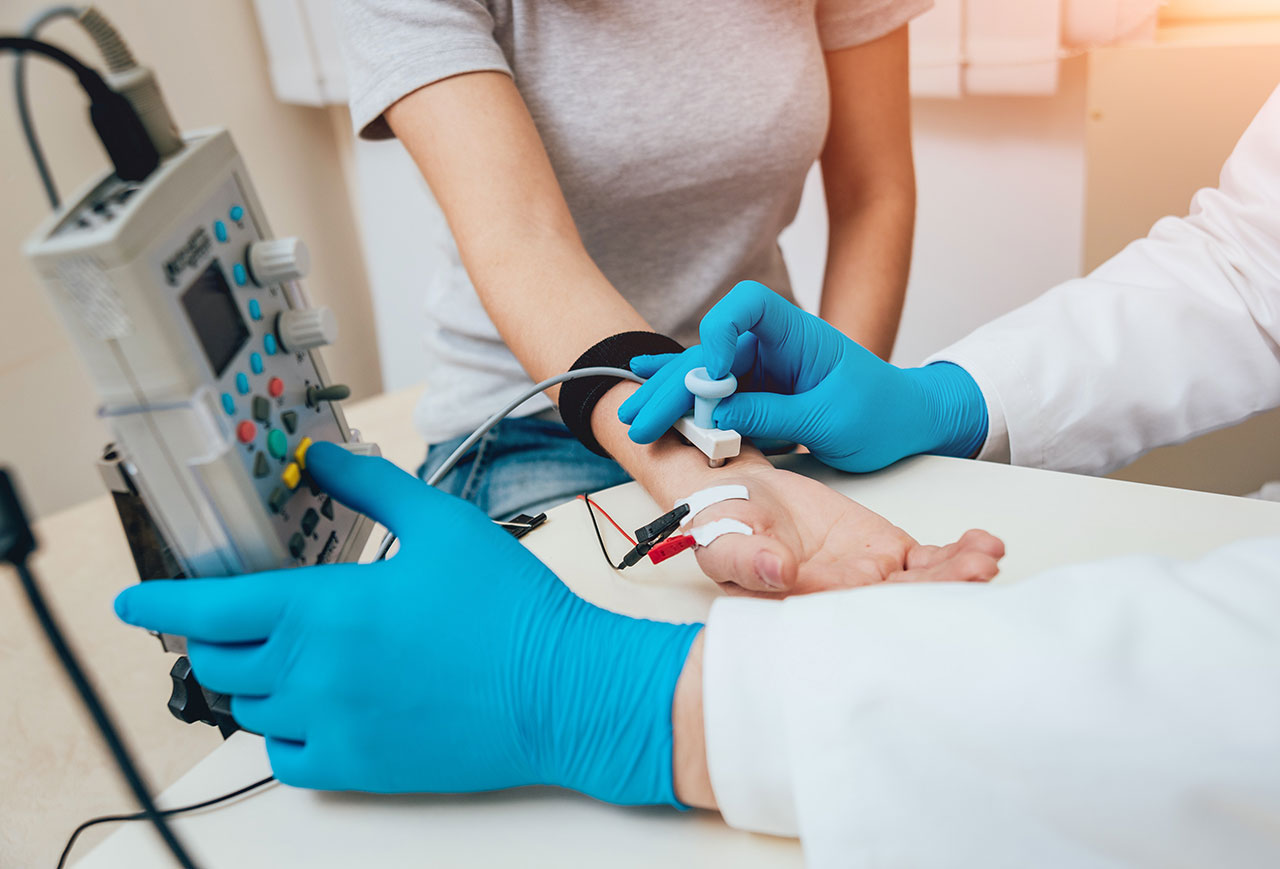
2. Nerve Tests
A nerve conduction study is a medical diagnostic test that is commonly used to assess the function, especially the ability of electrical conduction, of the motor and sensory nerves of the body.
There are two different types of nerve tests:
- Electromyography (EMG) – In electromyography, electrical recordings and activity of the nerves are measured by inserting tiny needles into the muscles.
- Nerve conduction studies – In nerve conduction studies, mild electric shock is given to activate the nerves and check how fast signals travel through them.
In GBS, abnormal nerve conduction velocity findings, such as slow signal conduction, are usually observed.
Get IVIG Prior Authorization
3. Lumbar Puncture
In this medical procedure, also known as a spinal tap, a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most typically to collect cerebrospinal fluid for diagnostic testing purposes. Lumbar punctures help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including those of the brain and spine. Key diagnostic findings include elevated cerebrospinal fluid protein without elevated cell count. It may take up to 10 days from the onset of symptoms for this to develop.
4. Antibody Tests
An antibody test on blood is done to identify if the patient has the Miller Fisher variant of Guillain-Barre syndrome. However, there are limitations to antibody tests, and they are usually not available for identifying the more common types of Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Contact Us
By submitting, you agree to AmeriPharma’s Terms of Use, Privacy Policy, and Notice of Privacy Practice.
This information is not a substitute for medical advice or treatment. Talk to your doctor or healthcare provider about your medical condition prior to starting any new treatment. AmeriPharma Specialty Care assumes no liability whatsoever for the information provided or for any diagnosis or treatment made as a result, nor is it responsible for the reliability of the content.
AmeriPharma Specialty Care does not operate all the websites/organizations listed here, nor is it responsible for the availability or reliability of their content. These listings do not imply or constitute an endorsement, sponsorship, or recommendation by AmeriPharma Specialty Care.
This webpage may contain references to brand-name prescription drugs that are trademarks or registered trademarks of pharmaceutical manufacturers not affiliated with AmeriPharma Specialty Care.

Dr. Rachel Chang, PharmD was born and raised in Hawaii. She received her degree from Marshall B. Ketchum University in 2022, where she graduated with cum laude honors. The most rewarding part of her job is the connections she makes with each patient. She enjoys speaking with each patient and helping them achieve the best treatment possible. In her free time, she likes spending time with her family, traveling, fishing, and mountain biking.